Click Create Assignment to assign this modality to your LMS. From Massachusetts to Mississippi a unicellular protist is hinting at answers about the evolution of multicellularity while raising a.
Do All Animals On Earth Descend From A Single Common Ancestor Or Could We Have Evolved From Multiple Common Ancestor Animals That Developed Separately Quora
Scientists think that protists are the oldest eukaryotes.
. Jawless fish have a simpler hemoglobin than do jawed fish which in turn have a simpler hemoglobin than mammals. Our mission is to increase public and scientific understanding of the biological and environmental history of Earth through the study of fossil animals plants and protists. Evolution of Protists.
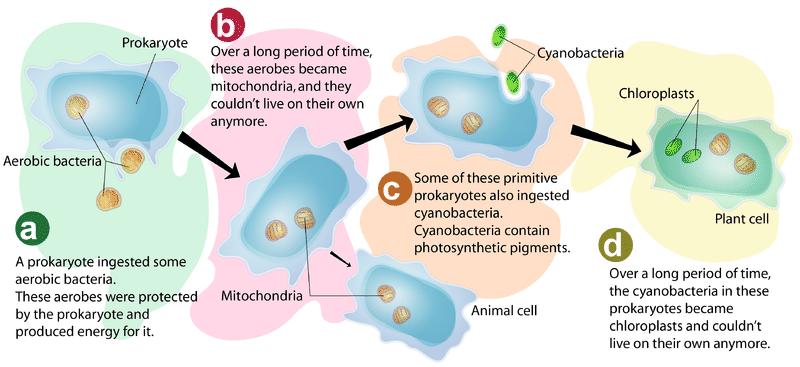
Because avoiding bitter plants would severely limit their food sources strict herbivores have fewer bitter taste genes than omnivores or carnivores. If so they must have evolved from prokaryotic cells. Two prokaryotic cells 1 form an early eukaryotic cell 3.
The fossil record in the form of shells in sedimentary rocks shows that protozoa were. Introduces evolution of the non-plant non-animal and non-fungi eukaryotes. The protists may also represent the ancestors of modern-day plants animals and fungi.
A proposal as to how eukaryotic cells evolved. The lineage which led to plants and most protists began with tubular mitochondrial cristae an anterior cilium and developed cellulose and cycloartenol Cavalier-Smith 2003. More than 50000 species have been described most of which are free-living organisms.
Origin of animals - Two theories. 800 million years ago. This system does to categorize them by their evolutionary history.
In early classification schemes they were clumped together and called protozoa to separate them from the more plantlike protists. The evolution of complex molecular systems can occur in several ways. Protists that obtain their food by external digestion Fungus-like protists.
In addition to performing scientific research we assemble and curate fossil collections that are studied by scientists from around the country and the world. The emerging classification scheme groups the entire domain Eukaryota into six supergroups that contain all of the protists as well as animals plants and fungi that evolved from a common ancestor. Organisms some scientists classify protists by their method of obtain-ing nutrition.
The larger cells then engulfed photosynthetic bacteria 6 gaining the ability to photosynthesize. Animals evolved by ingression from hollow spherical colonial flagellates. The body of an individual protist is simply pinched into two parts or halves.
The lineage which evolved into animals fungi and choanoflagelleates evolved flat mitochondrial cristae positioned the ancestral cilium in the posterior developed chitin and lanosterol. Animal-like protis ts plantlike protists and funguslike protists. Thats because it is well supported by evidence.
Plants are much more likely than animals to contain toxins. They have been implicated specifically in hypotheses of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic ancestries eukaryogenesis via endosymbiosis which in a broad sense might be considered an ecological factor in the very early evolution of organisms destined to compose the eukaryotic kingdoms. Though this protists-like ancestor is a hypothetical organism we can trace some genes found in modern animals and plants to these ancient organisms.
There are four separate phyla of protists with animal characteristics. By tracking the evolutionary history of these particular organisms were able to look at ancestral states of certain gene suites and thats the really important thingwe need a. It must be understood that these categories are an artificial way of organizing a very diverse group of organisms.
Complex biochemical systems can be built up from simpler systems through natural selection. This indicates how strong in your memory this concept is. Cell division in protists as in plant and animal cells is not a simple process although it may superficially appear to be so.
A protist ˈ p r oʊ t ɪ s t is any eukaryotic organism that is an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus that is not an animal plant or fungus. Metazoa evolved from multinucleate ciliates. Reproduction and life cycles.
The endosymbiotic theory provides the most widely-accepted explanation. Early eukaryotes 4 may have engulfed bacteria 5 and kept them inside their cell membranes giving rise to mitochondria. Protists are suspected to have played a key role in eukaryotic evolution.
The problem of protists. The typical mode of reproduction in most of the major protistan taxa is asexual binary fission. Prot ists are divided into three groups using this method.
The protozoan proh tuh ZOH un plural protozoa or protozoans shown in Figure 191 is an example of an animal-like protist because. While exceptions exist they are primarily microscopic and made up of a. Thus the history of a protein can be traced through simpler organisms.
It has also been suggested that due to lateral gene transfer a. A species is a group of individual organisms that interbreed and produce fertile viable offspring. A phylogenetic tree of living things based on RNA data and proposed by Carl Woese showing the separation of Bacteria Archaea and Eukaryota.
While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor the last eukaryotic common ancestor 2 the exclusion of other eukaryotes means that protists do not form a natural group or clade. Scientists speculate that protists form a link between plants animals and fungi as these three kingdoms diverged from a common protist-like ancestor billions of years ago. The early multicellular animals undergo their first splits.
According to this definition one species is distinguished from another when in nature it is not possible for matings between individuals from each species to produce fertile offspring. Members of the same species share both external and. The Protozoa are considered to be a subkingdom of the kingdom Protista although in the classical system they were placed in the kingdom Animalia.
The ability to discern bitter tastes evolved as a mechanism to prevent early humans from eating poisonous plants. How did this happen. The exact relationships of the three domains are still being debated as is the position of the root of the tree.
Discusses how protists evolved from prokaryotic cells. Protists are a diverse collection of organisms that do not fit into animal plant bacteria or fungi groups. The supergroups are believed to be monophyletic meaning that all organisms within each supergroup are believed to have evolved from a single common ancestor and thus all.
First they divide into essentially the sponges and everything else. Protozoa are found in almost every possible habitat. Humans have about.
Up to 24 cash back Heterotrophs Animal-like protists. The parental body disappears and is replaced by a pair of. Animals evolved from a multinucleate protociliate.
Protists that produce their own food Plant-like protists.
How Did Plants Affect The Evolution Of Animals Quora

Animal Evolution Ck 12 Foundation
Why Did Humans Animals Plants And Microorganisms Evolve Quora
Protist Evolution Ck 12 Foundation

Pin On Microbiology And Evolution


0 comments
Post a Comment